The Complete Guide to Predictive Maintenance for Beginners
A complete guide to what is predictive maintenance for beginners. Learn to prevent breakdowns, reduce costs, and apply it to BioGas processing systems.
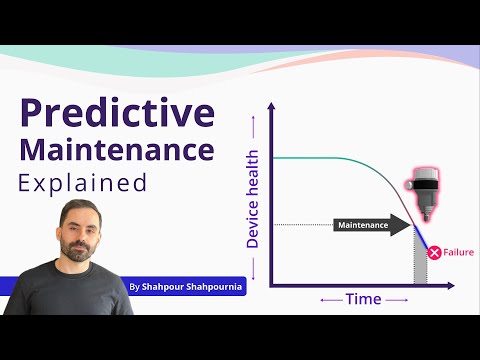
Predictive maintenance uses real time data from your equipment to predict when something will break before it actually happens. Instead of fixing machines after they fail or scheduling maintenance based on a calendar, you monitor conditions like temperature, vibration, and performance patterns. When the data shows signs of trouble brewing, you step in and fix the issue. This approach saves you from unexpected breakdowns and eliminates unnecessary maintenance work.
This guide walks you through everything you need to know about predictive maintenance. You'll learn why it matters for your operations, how to get started from scratch, and what technologies make it work. We'll cover the main benefits and risks, help you avoid common mistakes, and show you how predictive maintenance applies specifically to BioGas and BioMethane processing systems. By the end, you'll understand whether predictive maintenance makes sense for your equipment and how to implement it effectively.
Why predictive maintenance matters
Understanding what is predictive maintenance and why it matters starts with recognizing the true cost of equipment failure. When your machinery breaks down unexpectedly, you face immediate production losses, expensive emergency repairs, and potential safety hazards. Research from Deloitte shows that predictive maintenance can reduce facility downtime by 5 to 15% and increase labor productivity by 5 to 20%. These improvements directly impact your bottom line by keeping operations running smoothly and reducing maintenance spending.
Financial impact of equipment failures
Unplanned downtime costs companies an average of $260,000 per hour across industries, according to manufacturing data. Your repair bills multiply when you need emergency parts, overnight shipping, and overtime technician rates. Predictive maintenance helps you order replacement parts ahead of time at regular prices and schedule repairs during planned downtime windows. You avoid the panic of scrambling to fix critical equipment while production sits idle, which means you maintain consistent revenue streams and meet customer commitments.
Predictive maintenance transforms maintenance from a cost center into a strategic advantage by preventing failures before they disrupt your operations.
Extended equipment lifespan and improved safety
Equipment that runs under monitored conditions lasts significantly longer than machines that operate until failure. You extend the useful life of your assets by 20 to 40% when you address wear patterns early and maintain optimal operating conditions. This approach also protects your workforce from dangerous equipment failures that could cause injuries or environmental incidents. Predictive maintenance gives you visibility into potential hazards before they escalate, allowing you to take corrective action while conditions remain safe. Your teams work with reliable equipment, and you reduce the risk of catastrophic failures that could harm people or damage your facility.
How to get started with predictive maintenance
Getting started with predictive maintenance requires a strategic approach rather than deploying sensors across every piece of equipment you own. You need to evaluate your current situation, identify the best candidates for monitoring, and build your program incrementally. This systematic process helps you demonstrate value quickly while avoiding the overwhelm of trying to monitor everything at once.
Assess your current equipment and maintenance practices
Begin by documenting your existing maintenance activities and understanding where failures cost you the most. Review your maintenance logs, downtime records, and repair invoices from the past year to identify patterns. You want to find equipment that breaks down frequently, causes significant production losses, or requires expensive emergency repairs. This data reveals which assets would benefit most from continuous monitoring and predictive intervention.
Calculate the total cost of ownership for your critical equipment, including maintenance labor, spare parts, production losses, and energy consumption. Equipment with high failure rates or expensive repair costs becomes your priority target. You should also consider safety implications, as machinery that could harm workers or cause environmental damage deserves special attention regardless of direct financial impact.
Choose the right equipment to monitor
Focus your initial predictive maintenance efforts on assets that meet specific criteria for success. Your best candidates are machines with moving parts, high operating temperatures, or components that wear gradually over time. Equipment like pumps, compressors, motors, and heat exchangers typically provides clear warning signs before failure through changes in vibration, temperature, or performance metrics.
Avoid starting with equipment that fails randomly or has minimal impact on your operations. Simple assets with low replacement costs or machines that sit idle most of the time don't justify the investment in predictive monitoring. You'll achieve better results by concentrating your resources on critical production equipment where preventing a single failure pays for the entire monitoring system.
Start small and scale gradually
Launch your predictive maintenance program with one to three pieces of equipment rather than attempting a facility-wide rollout. This focused approach lets you learn what is predictive maintenance in practice, refine your processes, and build expertise before expanding. You can test different monitoring technologies, establish baseline performance data, and develop response protocols without overwhelming your maintenance team.
Starting small allows you to prove the concept, secure stakeholder support, and build organizational confidence before scaling your predictive maintenance program.
Track your results meticulously during this pilot phase by measuring downtime avoided, maintenance costs saved, and production improvements gained. Document every instance where predictive insights prevented a failure or allowed you to schedule repairs at convenient times. These success stories become powerful tools for securing budget and support to expand your program to additional equipment. Your maintenance team also builds the skills and confidence needed to interpret sensor data, recognize warning signs, and take appropriate action based on predictive alerts.
Key concepts and technologies in predictive maintenance
Understanding what is predictive maintenance means grasping the core technologies that make it work. Your predictive maintenance system relies on three essential components: sensors that gather data from equipment, networks that transmit this information to processing systems, and analytics software that interprets patterns and generates actionable insights. These technologies work together to create a continuous monitoring system that watches your equipment around the clock and alerts you when conditions indicate potential failure. You don't need to understand every technical detail, but knowing how these pieces fit together helps you make informed decisions about implementing predictive maintenance in your facility.
Condition monitoring techniques
Different types of equipment require different monitoring approaches based on how they operate and how they typically fail. Your monitoring strategy should match the specific failure modes you want to prevent. Vibration analysis works best for rotating equipment like motors, pumps, and compressors because changes in vibration patterns reveal imbalance, misalignment, or bearing wear before these issues cause failure. You can detect problems weeks or months in advance by tracking vibration frequency and amplitude.
Thermal imaging captures temperature variations across equipment surfaces to identify hotspots that indicate electrical problems, friction, or inadequate lubrication. This technique proves valuable for electrical systems, heat exchangers, and any equipment where temperature changes signal deterioration. Acoustic monitoring listens for changes in sound patterns, helping you find air leaks, steam leaks, or mechanical problems that produce audible or ultrasonic frequencies. Oil analysis examines lubricant condition and detects metal particles that indicate internal wear, making it essential for gearboxes and hydraulic systems.
IoT sensors and data collection
Your predictive maintenance program depends on IoT sensors that continuously measure equipment conditions and transmit data to central monitoring systems. These sensors attach to your equipment and measure specific parameters like temperature, vibration, pressure, flow rate, or electrical current. Modern sensors connect wirelessly to your network, eliminating the need for complex wiring installations and allowing you to monitor equipment in remote or difficult-to-reach locations.
Sensors transform your equipment into connected assets that communicate their health status in real time, giving you unprecedented visibility into operational conditions.
You can retrofit existing equipment with sensors using gateway devices that bridge the gap between older analog machinery and modern digital networks. These gateways collect data from multiple measurement points and package it for transmission to your monitoring system. Cloud connectivity enables you to access equipment data from anywhere, view trends over time, and receive alerts on your smartphone when sensors detect abnormal conditions. Your sensors generate massive amounts of data every minute, creating the foundation for accurate predictions.
Analytics and machine learning
Raw sensor data becomes valuable only when analytics software processes it to identify meaningful patterns and predict future equipment behavior. Your predictive maintenance system uses algorithms that compare current equipment performance against baseline conditions established during normal operation. When measurements deviate from expected patterns, the system flags these anomalies as potential warnings of developing problems. You receive alerts ranked by severity so you can prioritize your response based on urgency and potential impact.
Machine learning enhances predictive accuracy by studying historical data to recognize patterns that precede specific types of failures. Your system learns which combinations of temperature, vibration, and performance metrics typically occur before a bearing fails or a seal leaks. Over time, these algorithms become more accurate as they analyze more data and observe more equipment cycles. Advanced systems can predict not just that a failure will occur, but when it will happen, giving you precise windows for scheduling maintenance during planned downtime periods.
Benefits, risks, and common mistakes
Implementing predictive maintenance delivers measurable improvements across your operations, but you need to understand both the advantages and potential pitfalls before committing resources. Your success depends on realistic expectations about what predictive maintenance can achieve and awareness of common implementation challenges that derail programs. This section helps you maximize benefits while avoiding the mistakes that cause many organizations to abandon their predictive maintenance initiatives before achieving meaningful results.
Quantifiable business benefits
Your predictive maintenance program delivers direct cost savings through reduced downtime, lower maintenance expenses, and extended equipment life. Research shows facilities achieve 10 to 20% reductions in maintenance costs by eliminating unnecessary preventive tasks and avoiding expensive emergency repairs. You optimize spare parts inventory because predictive insights let you order components only when data indicates actual need, reducing the capital tied up in just-in-case parts storage.
Production improvements represent another major benefit category as your equipment runs more reliably and efficiently. You increase overall equipment effectiveness by 5 to 15% when machines operate at optimal performance levels without unexpected interruptions. Your teams shift from reactive firefighting to planned maintenance activities, improving workplace safety and reducing stress from constant emergency responses. Energy consumption often decreases when you maintain equipment in peak condition, as worn components typically require more power to deliver the same output.
Implementation risks to avoid
Understanding what is predictive maintenance includes recognizing the upfront investment required for sensors, software, and training. You risk wasting money if you deploy monitoring systems without clear objectives or try to monitor equipment where predictive maintenance provides minimal value. Poor data quality undermines your entire program when sensors malfunction, connectivity fails, or baseline measurements prove inaccurate. Your predictions become unreliable, leading teams to ignore alerts and revert to old maintenance habits.
The biggest risk in predictive maintenance is not technical failure but organizational resistance when teams lack proper training and stakeholder support for the new approach.
Most common mistakes and how to prevent them
Your biggest mistake would be attempting facility-wide deployment without first proving the concept on a small scale. Organizations that start too big overwhelm maintenance teams, struggle to demonstrate clear ROI, and lose leadership support when results take too long to materialize. You prevent this by beginning with three to five critical assets where success seems most likely and expanding only after documenting concrete improvements.
Another common error involves collecting data without acting on insights generated by your monitoring systems. Your predictive maintenance program fails when alerts go unaddressed because teams lack authority, resources, or processes to respond. You need clear escalation procedures, spare parts availability, and management commitment to schedule maintenance based on predictive recommendations rather than convenience. Ignoring your predictive system's warnings teaches your team that the data doesn't matter, destroying the program's credibility and value.
Predictive maintenance for BioGas and BioMethane systems
BioGas and BioMethane processing systems present unique monitoring requirements because they handle corrosive gases, operate under varying feedstock conditions, and must maintain strict purity standards. Understanding what is predictive maintenance in this context means recognizing that your equipment faces challenges unlike standard industrial machinery. Your compressors, heat exchangers, catalytic reactors, and desulphurization units endure continuous exposure to hydrogen sulfide, moisture, and organic compounds that accelerate wear patterns. Predictive monitoring becomes essential when equipment failure could compromise gas quality, violate pipeline specifications, or create safety hazards from leaks or pressure system failures.
Critical equipment components to monitor
Your BioGas booster systems require continuous vibration and temperature monitoring because these compressors operate at demanding pressures while handling contaminated gas streams. Bearing wear, seal degradation, and valve problems typically announce themselves through subtle changes in vibration patterns before causing catastrophic failure. You should also monitor your catalytic reactors for temperature uniformity and pressure drops that indicate catalyst fouling or degradation. These systems must maintain precise operating conditions to achieve oxygen removal targets below 10 ppm in your final BioMethane product.
Heat exchangers and moisture removal systems need monitoring for differential pressure and thermal efficiency as fouling reduces heat transfer capacity. Your membrane or amine-based CO2 separation equipment shows performance decline through changes in pressure differentials and separation efficiency metrics. Predictive monitoring catches these degradation patterns early, allowing you to schedule cleaning or membrane replacement during planned shutdowns rather than experiencing unexpected product quality failures.
Unique challenges in BioGas processing
Corrosive compounds in raw BioGas create accelerated equipment wear compared to conventional natural gas processing. Your desulphurization catalysts degrade over time, reducing H2S removal efficiency and potentially allowing sulfur compounds to reach downstream equipment where they cause damage. Variable feedstock composition from anaerobic digesters means your equipment experiences fluctuating loads, temperatures, and contaminant levels that complicate baseline establishment for predictive algorithms.
Predictive maintenance in BioGas systems must account for feedstock variability and corrosive operating conditions that create unique failure patterns not seen in conventional gas processing.
Predictive strategies for optimal performance
You achieve maximum uptime by integrating predictive monitoring directly into your control systems rather than treating it as a separate maintenance function. Modern BioGas processing equipment includes built-in sensors and remote monitoring capabilities that track critical parameters continuously. Your predictive strategy should focus on performance trending rather than just equipment health, because declining separation efficiency or rising energy consumption often indicates developing problems before component failure occurs. You can establish performance baselines during commissioning and set alert thresholds at 5% degradation from optimal conditions, giving yourself weeks to plan interventions before reaching critical failure points.
Key takeaways
You now understand what is predictive maintenance and how it transforms equipment management from reactive firefighting to proactive planning. Your success depends on starting small with critical assets, collecting quality data through appropriate sensors, and acting on the insights your monitoring systems generate. Implementation requires upfront investment in technology and training, but the returns through reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and extended equipment life justify this commitment across most industrial applications. Focus your initial efforts on equipment where failure causes the greatest operational and financial impact.
BioGas and BioMethane processing systems particularly benefit from predictive monitoring because corrosive operating conditions and variable feedstocks accelerate equipment wear. Your processing equipment needs continuous condition monitoring to maintain product quality and prevent unexpected failures that compromise operations. Explore how 99pt5's BioTreater™ system integrates advanced monitoring and automation to deliver guaranteed 99.5% BioMethane recovery with industry-leading reliability and the lowest operating expenses in the market.